Disrupted Gut Microbiome Promotes Breast Cancer Spread In Mice
Written by Victoria Forster
 The health of the gut microbiome has been linked with numerous diseases from depression to multiple sclerosis and even cancer and response to cancer drugs including immunotherapies. Earlier this year, an ambitious $25 million project was launched to determine the role of the microbiome in colorectal cancer, but perhaps more surprisingly, a new study in mice has linked the health of the gut microbiome to the spread of breast cancer. Read more.
The health of the gut microbiome has been linked with numerous diseases from depression to multiple sclerosis and even cancer and response to cancer drugs including immunotherapies. Earlier this year, an ambitious $25 million project was launched to determine the role of the microbiome in colorectal cancer, but perhaps more surprisingly, a new study in mice has linked the health of the gut microbiome to the spread of breast cancer. Read more.
Researchers identify faster, more effective drug combination regimens to treat tuberculosis
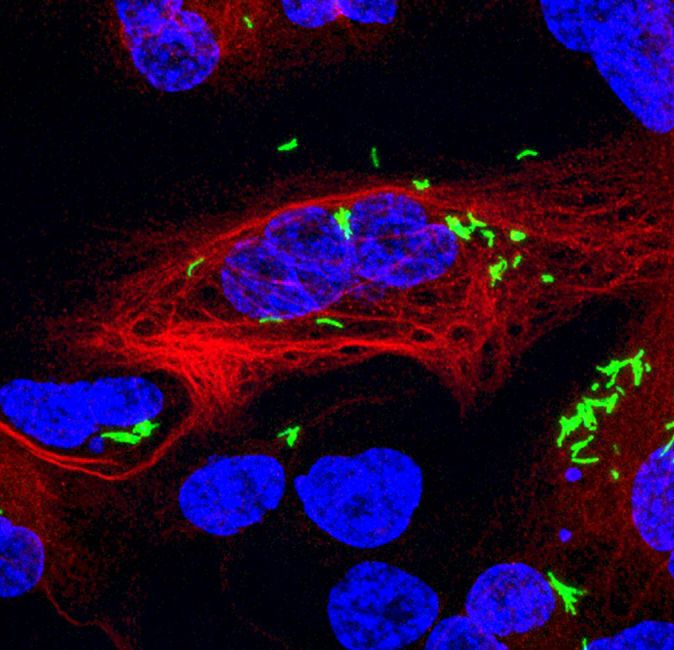
Human white blood cells infected with tuberculosis bacteria, shown in green. Photo credit: UCLA D.L. Clemens
Written by Enrique Rivero
Tuberculosis is a potentially deadly though curable disease. Each year about 10 million people develop active cases, and 1.6 million people die. In addition, about 1.7 billion people around the world are infected with TB bacteria, which can lie dormant for weeks to years, then become active and cause disease in up to 10 percent of those who are infected.
Today, people who contract tuberculosis typically take a course of drugs for six to eight months. However, the length of treatment means some patients don’t stick with the therapy or may develop adverse effects from drug toxicity. Some may develop resistance to the drugs, requiring changes in the drug regimen that can lengthen the treatment to as long as two years. Even worse, there is a high fatality rate among those with drug-resistant TB. Read more.
Study: Sleep Deprivation Speeds Up Alzheimer’s Disease

Photo credit: Stock photo
Written by Claire Hansen
Experts have long warned about the negative effects of sleep deprivation, and new research suggests that people with Alzheimer’s disease may be particularly affected.
In a study of mice and humans, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found that sleep deprivation increases levels of the protein tau, which is linked to Alzheimer’s disease. In follow-up studies in mice, the researchers also found that sleeplessness speeds up the spread of toxic clumps of tau in the brain, a precursor to brain damage and dementia. Read more.
A Diabetes Drug Has ‘Significantly Reversed Memory Loss’ in Mice With Alzheimer’s
Written by: Fiona MacDonald

A drug developed for type 2 diabetes has “significantly reversed memory loss” in mice with Alzheimer’s disease, and researchers now want to test it on humans.
The treatment is exciting for scientists because it works by protecting the brain cells attacked by Alzheimer’s disease in three separate ways, rather than relying on a single approach.
And seeing as the drug has already been tested and approved for use in humans, it’s something that could hit the market a lot faster than other experimental treatment options. Read more.